Dermatitis Herpetiformis
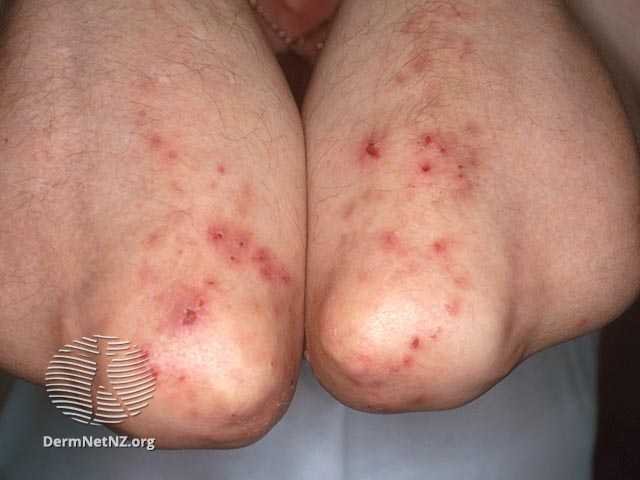
Dermatitis Herpetiformis often displays as itchy blisters on the elbows, knees and buttocks.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is dermatitis herpetiformis?
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic skin condition characterized by intensely itchy, blistering rashes, predominantly found on the elbows, knees, and buttocks. It is closely linked to celiac disease, a digestive disorder caused by an abnormal immune response to gluten. Those with DH often have gluten sensitivity in their intestines, even if they don't show gastrointestinal symptoms.
What causes dermatitis herpetiformis?
Dermatitis herpetiformis is associated with an immune system response to gluten ingestion. When individuals with a predisposition consume foods containing gluten, their immune system reacts by producing specific antibodies. These antibodies deposit in the skin, leading to the itchy and blistering rash of DH. It is noteworthy that the majority of those with DH also have evidence of celiac disease on intestinal biopsy, even if they don't manifest gastrointestinal symptoms.
What are the symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis?
The primary symptom of DH is a rash with red, raised patches and blisters filled with a clear fluid. Other characteristics and symptoms include:
Intense itching: Often the first noticeable symptom
Symmetrical rash: Appears on both sides of the body
Common sites: Elbows, knees, buttocks, scalp, and back
Periodic outbreaks: Flare-ups can occur periodically, sometimes triggered by gluten consumption
Digestive symptoms: Though less common, some may experience celiac disease-associated symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss
How is dermatitis herpetiformis treated?
Effective management of DH involves addressing both the skin symptoms and underlying gluten sensitivity. Treatment options include:
Dapsone: An antibiotic that provides rapid relief from itching and rash, but does not address the intestinal damage from gluten
Gluten-free diet: Adhering to a strict gluten-free diet can help resolve both skin and intestinal symptoms. It may also decrease or eliminate the need for medications.
Topical creams: Steroid creams can help reduce inflammation and itching
Regular monitoring: Given the association with celiac disease, those with DH often undergo periodic medical check-ups, including intestinal biopsies, to monitor the condition's status and potential intestinal damage.
How do I prevent flare-ups of dermatitis herpetiformis?
The most effective way to prevent DH flare-ups is by maintaining a strict gluten-free diet. This not only minimizes skin symptoms but also reduces the associated risk of intestinal damage. Regular consultation with a dermatologist and gastroenterologist can provide guidance on dietary adjustments and monitor the overall health of individuals with DH.
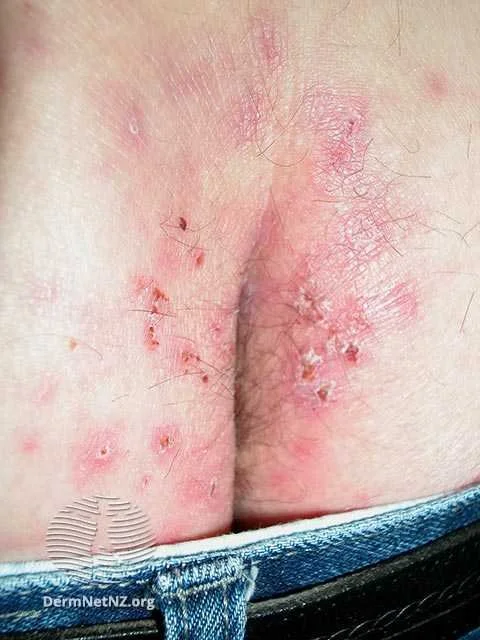
Dermatitis Herpetiformis often will present on the buttocks.
Credit: DermNet NZ
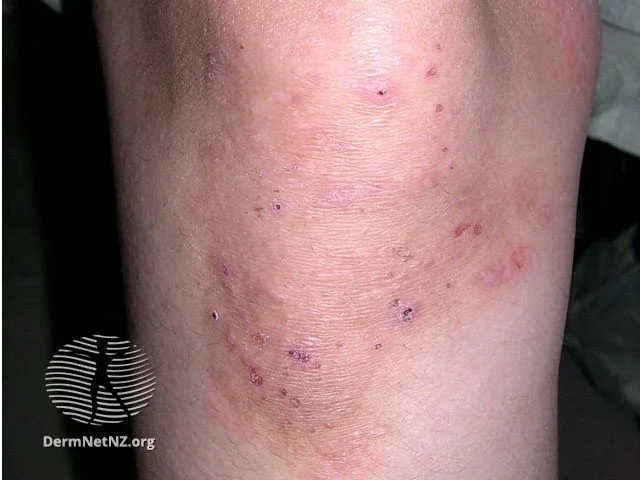
Dermatitis Herpetiformis can be mistaken for multiple other conditions since it is often scratched over.
Credit: DermNet NZ