Cysts
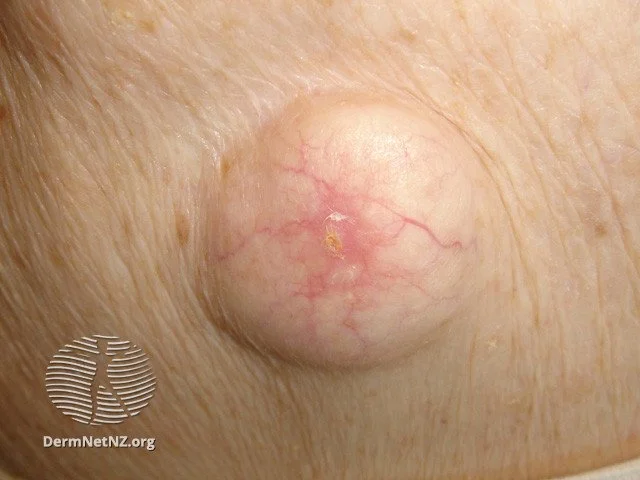
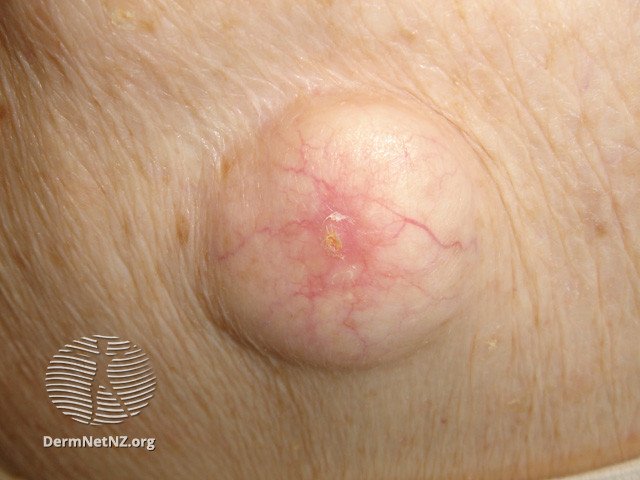
Large cyst, with central punctum (opening). Since it has grown slowly, there is blood vessel development on it.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What are cysts?
A cyst is a closed sac-like structure within the skin or other tissues, which may contain fluid, keratin, oil, air, or other substances. Unlike abscesses, which are primarily filled with pus, cysts are more complex. However, cysts can become infected, leading to the accumulation of pus and resulting in inflammation. Common types of cysts include epidermoid cysts, dermoid cysts, pilar cysts, milia, and mucoceles.
What causes cysts?
Cysts can form in various parts of the body and arise from multiple causes. In the context of the skin, cysts often develop when hair follicles, pores, or oil glands become obstructed. They can also arise when the skin's outermost layer grows inwards, rather than outwards. While the exact etiology of some cysts remains uncertain, factors such as genetics, hormonal fluctuations, physical trauma, acne, or hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) can contribute to their formation.
What are the symptoms of cysts?
Cysts typically present as round, palpable structures beneath the skin's surface. They can vary in size and may be soft or firm to the touch. While many cysts are asymptomatic, some might be tender or painful, especially if inflamed or infected. Infected cysts may also appear reddened, feel warm, and be swollen.
How do I treat cysts?
Effective treatment of cysts usually involves their complete surgical excision, ensuring both the sac and its contents are removed. If any part of the cyst remains post-extraction, there's a likelihood of recurrence. For temporary relief, particularly in the case of an inflamed or infected cyst, an incision can be made to drain its contents, or it can be injected with steroids. However, these are not definitive solutions most of the time, as these cysts tend to recur and can become infected again. Thus, it is advisable to consult with an experienced dermatologist for cyst removal. If a cyst becomes infected, oral antibiotics might be prescribed to combat the infection.
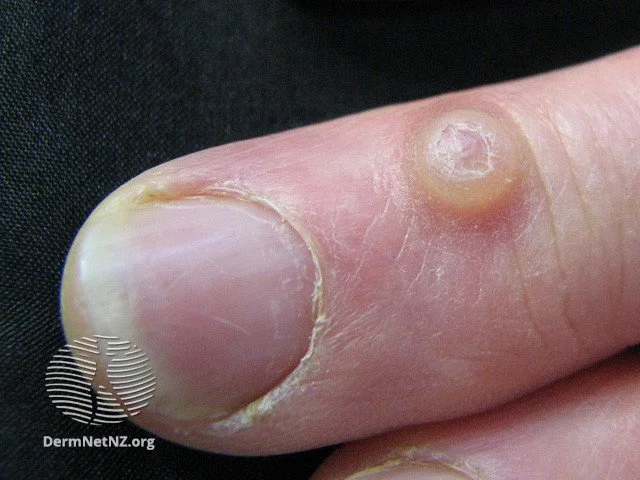
Digital Mucous Cysts are common at the end of the finger, can be mistaken for warts, and sometimes can cause nail irregularities.
Credit: DermNet NZ
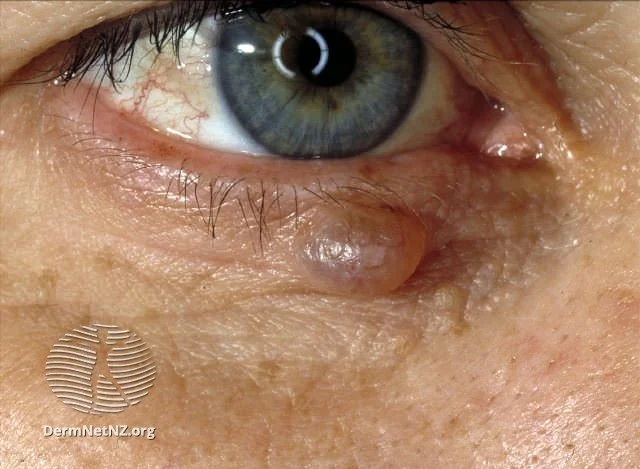
Hidrocystomas are thin-walled cysts that are common around the eyelids.
Credit: DermNet NZ