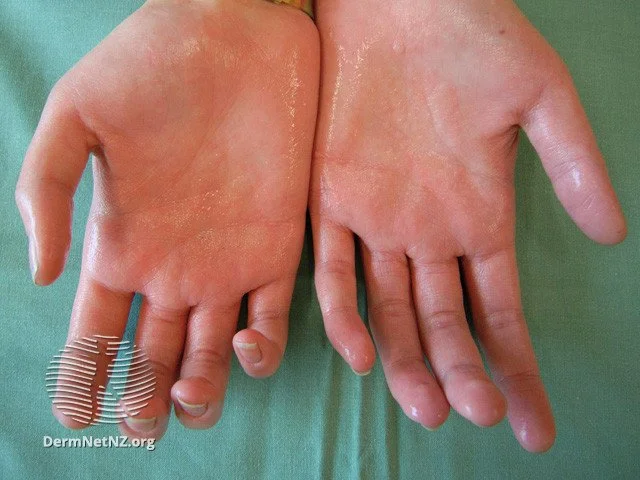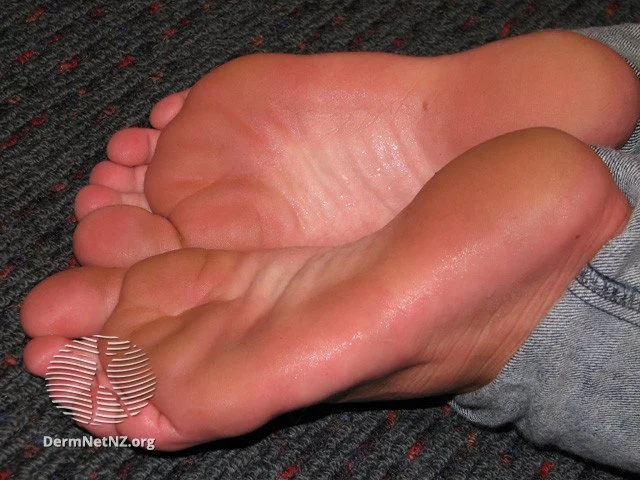
Hyperhidrosis
An example of hyperhidrosis, which appears as excessively sweaty skin most commonly on the armpits, hands, and feet.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition where individuals experience excessive sweating beyond what is needed to regulate body temperature. This condition can be generalized, affecting the entire body, or localized to specific areas like the hands, feet, armpits, face, and genital region. Typically starting during childhood or teenage years, it may have a genetic component. The excessive sweating can lead to skin complications such as irritation, fungal infections, or dehydration. Additionally, it can produce odor, making it a socially distressing condition for many.
What causes hyperhidrosis?
The root cause of hyperhidrosis can differ from person to person. When the cause remains unidentified, it is labeled as primary hyperhidrosis. This form usually starts in childhood, predominantly impacts the armpits, palms, or soles symmetrically, and tends to subside during nighttime. On the other hand, if the condition is induced by another medical issue or medication, it is termed secondary hyperhidrosis. Medical conditions potentially linked to hyperhidrosis include:
Medication side effects (e.g., from caffeine, alcohol, morphine, some antidepressants, or antipsychotics)
Anxiety disorders
Diabetes
Gout
Cardiovascular diseases
Hormonal shifts
Infections
Thyroid disorders
Certain cancers
What are the symptoms of hyperhidrosis?
The hallmark of hyperhidrosis is excessive, uncontrollable sweating. It can be:
Localized: Targeting specific regions like the armpits, hands, feet, face, etc.
Generalized: Affecting nearly the entire body.
How do I treat hyperhidrosis?
Managing hyperhidrosis is contingent on its severity, location, and the level of discomfort it causes. For cases where the condition is a side effect of another ailment or drug, addressing that root issue is crucial. Here are some general and medical measures for hyperhidrosis:
Use of prescription-strength antiperspirants
Topical or oral medications that reduce sweating, like anticholinergics (eg. glycopyrrolate)
Iontophoresis: A treatment using water to conduct a mild electrical current through the skin's surface
Medications like beta blockers
Botox injections to reduce sweating
Surgical interventions to excise sweat glands or the nerves activating them (reserved for extreme cases)
How do I prevent hyperhidrosis?
While it's challenging to prevent hyperhidrosis entirely, these steps may help mitigate its effects:
Achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Limit caffeine and alcohol intake.
Engage in regular physical activity.
Hyperhidrosis can affect the hands and feet commonly, but it can also be generalized.
Credit: DermNet NZ