Genital Herpes
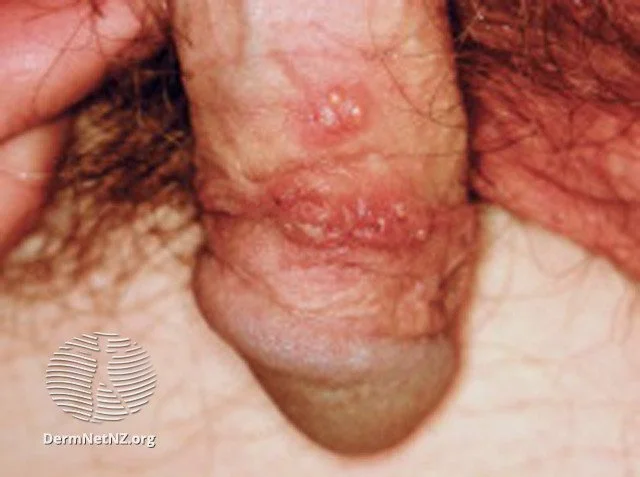
An example of genital herpes, with fluid-filled water blisters on a red base on the penis.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is genital herpes?
Genital herpes is a common and persistent sexually transmitted infection (STI) marked by recurring outbreaks of blisters and sores in the genital and surrounding areas. It impacts both men and women, but the presentation and locations of the lesions can differ:
Males: On the glans, foreskin, or the shaft of the penis.
Females: On the external genitalia, and the inner linings of the vulva, vagina, and cervix.
What causes genital herpes?
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two strains of this virus:
HSV-1: Primarily linked with oral herpes or cold sores but can also lead to genital herpes due to oral-genital contact.
HSV-2: The main culprit behind genital herpes, transmitted predominantly through sexual activity.
How is it transmitted?
The virus spreads mainly through:
Genital-genital contact with an infected individual.
Genital-oral contact, such as during oral sex.
Genital-anal contact.
What are the symptoms of genital herpes?
Infected individuals might experience recurring outbreaks characterized by:
Painful blisters and sores in the genital area.
Itching or burning sensation around the genitals.
Swollen lymph nodes.
Fever and flu-like symptoms, especially during the initial outbreak.
How do I treat genital herpes?
There's no cure for herpes, but antiviral medications can:
Alleviate symptoms.
Reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks.
Decrease the risk of transmitting the virus to sexual partners.
How do I prevent genital herpes?
To reduce the risk of acquiring or transmitting genital herpes:
Use latex condoms during intercourse.
Avoid sexual activity during outbreaks.
Regularly get screened for STIs.
Inform potential partners about your condition.
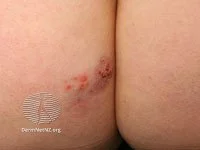
Genital herpes often can present as recurrent breakouts on the buttocks.
Credit: DermNet NZ
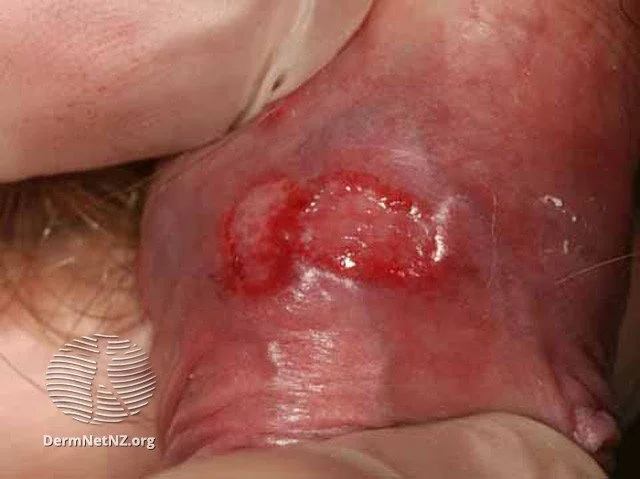
First time breakouts can be particularly severe.
Credit: DermNet NZ