Fungal Infections (Tinea, Ringworm)
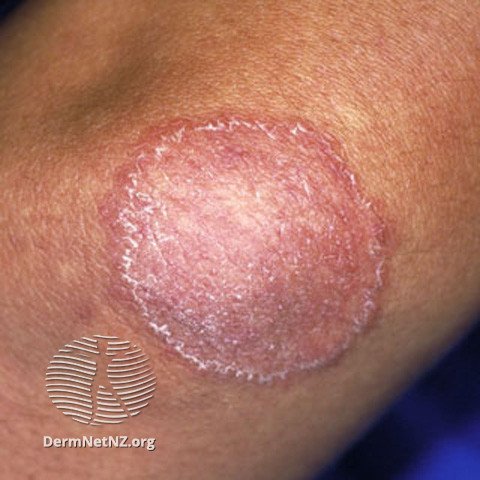
An example of tinea corporis, a type of fungal infection. Note the ring-like shape with the accentuation of scaliness to the edges.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What are fungal infections?
Fungal infections represent a group of common skin conditions instigated by various fungi. They typically manifest as an itchy, circular rash that's red and scaly, often with a clear center. These infections thrive in warm, damp environments and can spread via direct contact with an infected person, object, or even pets. The predisposition of infection increases if the skin is damaged or consistently wet. Specific forms of fungal infections based on their locations include:
Scalp (tinea capitis)
Beard (tinea barbae)
Body (tinea corporis, often called ringworm)
Groin (tinea cruris, known also as jock itch or diaper rash in infants)
Nail (onychomycosis, this can be challenging to treat)
What causes fungal infections?
These infections stem from dermatophytes – a specific type of fungi. While there are numerous fungi that can cause these infections, many display similar characteristics. Several risk factors make certain individuals more susceptible:
Excessive perspiration
Engaging in contact sports
Residing in humid, crowded environments
Unregulated diabetes
Wearing tight, non-breathable attire
Having a compromised immune system (due to HIV or particular medications)
What are the symptoms of fungal infections?
The manifestation of fungal infections can differ based on the location and the individual's unique physiology. However, common symptoms entail:
Intense itching
A raised red ring often bordered by scales
Dry and flaky skin surrounding the affected region
Potential hair loss in the infected area
Occasional presence of small, pus-filled blisters, especially in hair or beard regions
How do I treat fungal infections?
For most fungal infections affecting the skin, topical antifungal treatments are recommended. These include:
Tolnaftate
Ketoconazole or clotrimazole creams
Terbinafine ointment
In cases of severe symptoms, a steroid cream might be advised to alleviate discomfort. However, it's crucial to use these cautiously as they might aggravate the infection. Persistent or severe infections may necessitate oral medications like itraconazole, terbinafine, or ketoconazole.
How do I prevent fungal infections?
Staving off fungal infections primarily involves maintaining skin cleanliness and dryness. Best practices include:
Sanitizing hands post-interaction with animals, soil, or vegetation
Steering clear of contact with others' rashes
Opting for breathable, loose attire
Upholding rigorous personal hygiene routines
Using antifungal sprays proactively in footwear
An example of tinea versicolor, a type of fungal infection that can make the skin look white and scaly, and not pick up color in the sun.
Credit: DermNet NZ
An example of tinea barbae, a type of fungal infection, which can look like pimple-like bumps in hair-bearing areas.
Credit: DermNet NZ



