Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis, Tinea Unguium)
What is nail fungus?
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is an infection beneath the toenails and fingernails that can cause yellow or white discoloration, thickening, and crumbling of the nail. Its prevalence increases with age, and it often coexists with a fungal infection of the skin on the foot, termed "athlete's foot." While the latter can be treated relatively easily, nail fungus poses a greater treatment challenge. Although not perilous in itself, nail fungus may predispose individuals to bacterial infections of the foot and could be a source of discomfort or self-consciousness.
What causes nail fungus?
Nail fungal infections are usually caused by a variety of microorganisms, including dermatophytes (commonly linked to ringworm or fungal skin conditions), yeasts, and molds. Among them, dermatophytes are the most typical culprits. However, in humid and warm environments, yeasts may become more prevalent. Some predisposing factors for nail fungus are:
Advanced age
Prolonged exposure to moist conditions (e.g., wet socks/shoes)
Presence of psoriasis
Diabetes
Circulatory issues
What are the symptoms of nail fungus?
Nail fungus may manifest in one or multiple toenails or fingernails, typically targeting the big or little toe. Potential symptoms include:
A white or yellow streak on one side of the nail
Subungual scaling (scaling under the nail)
Nail detachment, leading to crumbling
White patches or pits on the nail's surface
Yellow discoloration at the lunula (half-moon region)
Nail thickening
Complete nail destruction
How do I treat nail fungus?
Effectively treating nail fungus, particularly on toenails, can be challenging due to the thick nail plate hindering treatment penetration. Mild infections might be addressed with topical antifungals, but severe cases often require extended courses of oral antifungals, which can present more side effects. Potential treatments encompass:
Topical antifungal agents (less efficacious): Such as ciclopirox nail lacquer and efinaconazole
Oral antifungal drugs (more potent but requiring careful monitoring): Such as terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole
Laser therapy for nail fungus
Complementary dilute vinegar foot soaks, used alongside primary treatments
How do I prevent nail fungus?
Reinfection is common among individuals previously affected by nail fungus. To minimize the risk:
Wear open-toed footwear generally
Use protective footwear in communal showers, swimming pools, etc.
Ensure feet are thoroughly dried after washing
Trim nails regularly and maintain good nail hygiene
Consider the application of over-the-counter antifungal powders or sprays
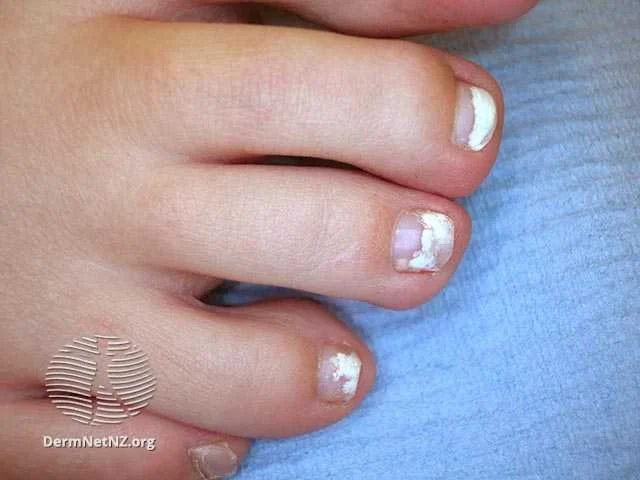
Superficial white onychomycosis is a type of nail fungus that sometimes can be more easily treated with topicals
Credit: DermNet NZ
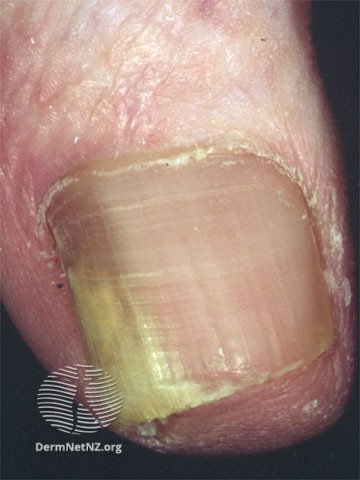
Sometimes nail fungus can also be caused by yeast in patients who are immunosuppresed.
Credit: DermNet NZ