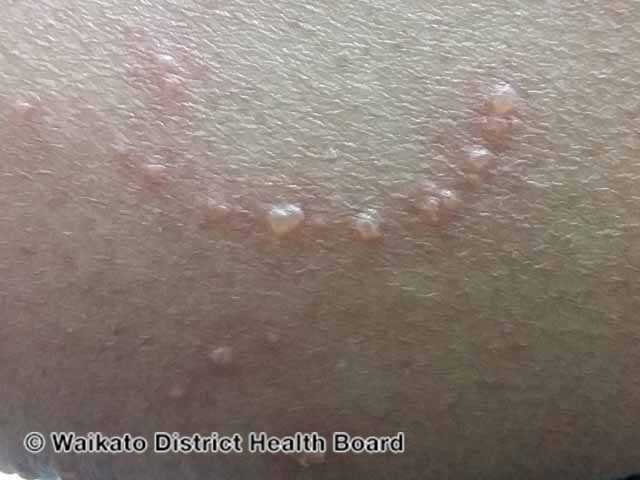
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum shows up as pimple-like bumps often on hot or sweaty areas. In the middle, you will see a small depression which is where the virus concentrates.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Manifesting as small, raised, painless pink bumps with a unique central dimple, it predominantly affects children. However, adults can acquire it, especially in the genital area through intimate encounters or if they have a compromised immune system.
What Causes Molluscum Contagiosum?
The primary causative agent is the molluscum contagiosum virus. It can spread via:
Direct skin-to-skin contact
Utilizing towels or other personal items that an infected person has used
Scratching or shaving an affected area, leading to self-transmission
Engaging in sexual contact with an infected person
What are the Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum?
The condition manifests as clusters of small, waxy, shiny bumps with a hallmark central dimple. These can range from 1 to 6 mm in size and can be white, pink, or brown, varying with skin color. When ruptured, they may release a white, cheese-like substance. They primarily appear in warm, moist regions, such as the armpits, behind the knees, groin, genitals, and sometimes, lips. Adjacent skin might become red and itchy, and the lesions can develop a crust or scab during the healing process.
How do I Treat Molluscum Contagiosum?
Although molluscum contagiosum might resolve independently over a span of up to 2 years, treatments are advisable due to the persistent infectious nature of the lesions. Treatment modalities include:
Cryotherapy, where lesions undergo freezing
Cantharidin application, done in a clinical setup
Topical preparations infused with podophyllotoxin or salicylic acid
Electrodessication or curettage for lesion removal, but these might leave scars
New approved treatments include Ycanth and berdazimer gel, but these can be expensive
How do I Prevent Molluscum Contagiosum?
To curb the transmission of molluscum contagiosum:
Regularly wash hands
Avoid scratching or touching the lesions
Ensure all lesions are covered with clothing or bandages and dispose of them after single use
Abstain from sharing personal belongings like towels
Always launder clothes post-wearing
Engage in safe sexual practices and contemplate abstinence if genital lesions are present
Molluscum is often more common in people with eczema prone skin.
Credit: DermNet NZ
Molluscum often heals with a characteristic pock-mark type scar that goes away over time.
Credit: DermNet NZ



