Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
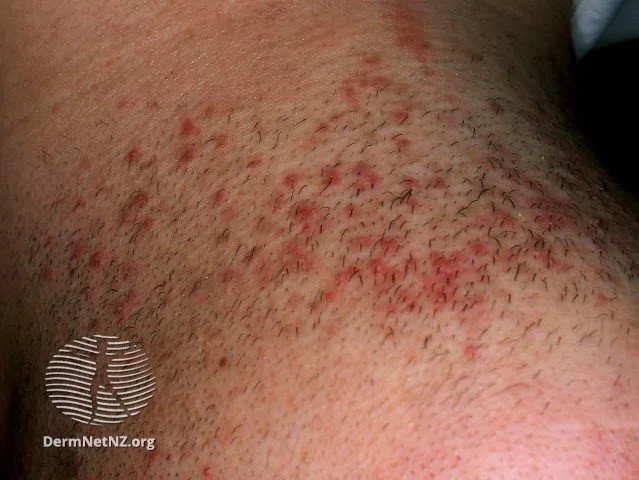
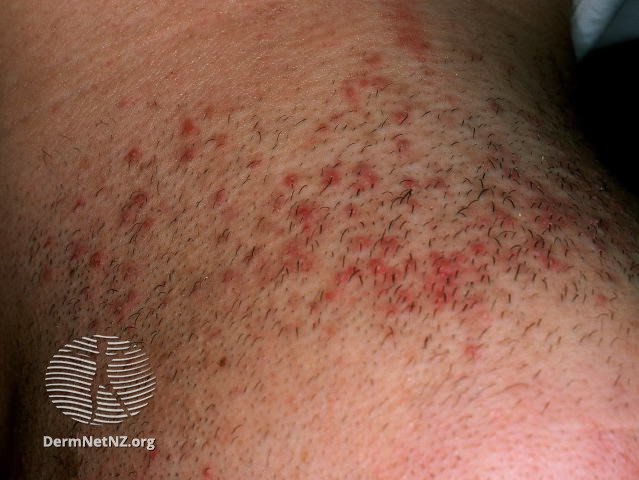
Pseudofolliculitis barbae presents as inflamed razor-burn type bumps in the beard area.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae, or PFB, commonly known as "razor bumps", is a skin condition characterized by small, irritated bumps that appear after shaving. The condition occurs when hair, after being cut, starts to grow back into the skin. This can lead to inflammation, pain, pustules, and even scar formation. It predominantly affects men with curly hair, especially African American men, but can be seen in anyone who shaves.
What causes Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
The primary cause of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae is the re-entry of growing hair into the skin:
Curly hair: Individuals with tightly curled hair are more prone as the hair is more likely to curl back and re-enter the skin.
Improper shaving techniques: Close shaves or pulling the skin taut during shaving can exacerbate the condition.
Friction: Rubbing of the area by clothing or other irritants.
What are the symptoms of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
The primary presentation of this condition involves skin lesions post-shaving:
Appearance: Small red or pigmented bumps on the shaved areas
Inflammation: Redness and swelling surrounding the bumps
Pustules: Pus-filled lesions may form in some cases
Itchiness: The area can be itchy and irritating
Pain: Especially when touched or when further shaving is attempted
How do I treat Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
Managing Pseudofolliculitis Barbae often involves a combination of preventive measures and treatments:
Avoid shaving: Letting hair grow can be an effective method, though not always practical.
Use the right technique: Use a single-blade razor, shave in the direction of hair growth, and avoid close shaves.
Topical treatments: Products containing hydrocortisone, glycolic acid, or salicylic acid can help reduce inflammation and bumpiness.
Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is present.
Laser hair removal: Offers a long-term solution by targeting the hair follicle.
Exfoliation: Helps remove dead skin cells and reduce ingrown hairs.
How do I prevent Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
Effective preventive measures can significantly reduce the incidence:
Proper shaving techniques: Not shaving against the grain and not stretching the skin.
Pre-shave preparations: Using a warm compress and a lubricating shaving gel can soften hairs.
Post-shave care: Applying a soothing moisturizer or astringent can help.
Electric razors: They don't cut as closely as blades, reducing the risk of ingrown hairs.
Regular exfoliation: Helps in preventing hair re-entry by removing dead skin cells.
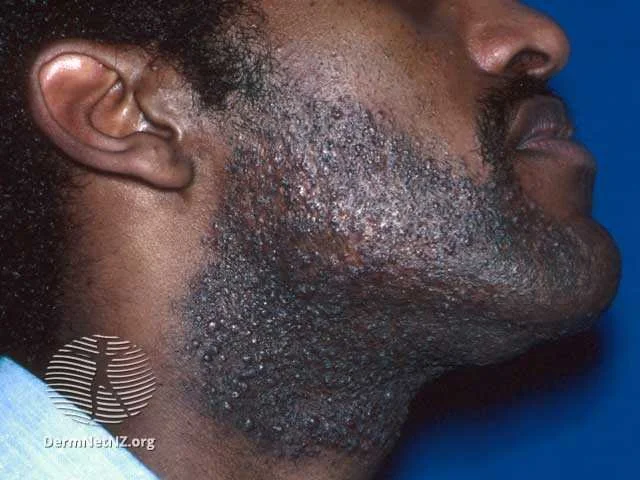
Pseudofolliculitis barbae can present with significant pigmentation and scarring.
Credit: DermNet NZ
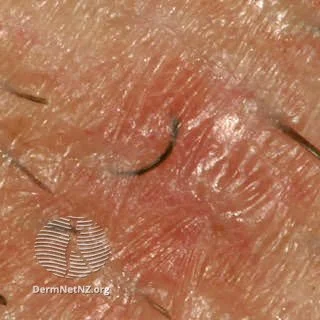
Ingrown hairs are generally the culprit for pseudofolliculitis barbae.
Credit: DermNet NZ