Urticaria (Hives)
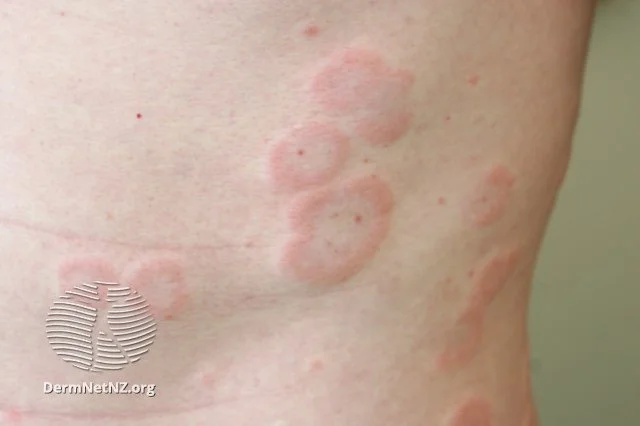
Hives or urticaria appear as itchy, swollen welt-like bumps and plaques on the body.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What Are urticaria?
Urticaria, often referred to as "hives," presents as areas of raised, itchy, and sometimes burning swellings on the skin, usually surrounded by redness. These hives can appear anywhere on the body and typically last from a few minutes up to 24 hours. While often linked to allergic reactions, the exact cause can vary. Chronic urticaria persists for more than 6 weeks. If someone with urticaria experiences sudden difficulty breathing, it is crucial to seek emergency medical care immediately.
What causes urticaria?
Urticaria can be classified as either acute (lasting less than 6 weeks) or chronic (persisting for more than 6 weeks). In both cases, the underlying mechanism involves the release of histamine, which causes blood vessels to expand and the skin to swell. While the exact trigger might not always be identified, some common causes include:
Acute Urticaria (<6 weeks):
Food allergies, commonly from milk, eggs, peanuts, or shellfish
Allergic reactions to medications, especially antibiotics
Insect stings or bites
Viral or bacterial infections
Environmental factors like cold, heat, or exercise
Pseudoallergies from certain medications, including aspirin, NSAIDs, opiates, and contrast dyes
Vaccinations
Contact with allergens, such as latex
Chronic Urticaria (> 6 weeks):
The exact cause is often unknown, but in roughly half the cases, autoimmune factors play a role. Other possible causes or associations include:
Chronic infections like H. pylori or bowel parasites
Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, celiac disease, or vitiligo
Thyroid diseases
Blood disorders
What are the symptoms of urticaria?
Urticaria manifests as raised, itchy, and occasionally burning skin patches. The surrounding area often appears reddened. Avoiding identified triggers is the primary preventive measure, while symptom relief remains the focus of most treatments.
How do I treat urticaria?
Treatment aims at both symptom relief and trigger avoidance. Common treatments include:
Non-sedating antihistamines (like loratadine, cetirizine, fexofenadine, or desloratadine)
Oral corticosteroids
Leukotriene-receptor antagonists (e.g., montelukast)
Dupilumab (off-label use)
Cyclosporin (for severe cases resistant to other treatments)
For those prone to urticaria, preventive measures include:
Treating underlying chronic infections, such as H. pylori
Avoiding NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen
Steering clear of confirmed allergens
Dressing warmly or avoiding cold exposure for cold-induced hives
Using sunscreen and protective clothing for sun-induced hives
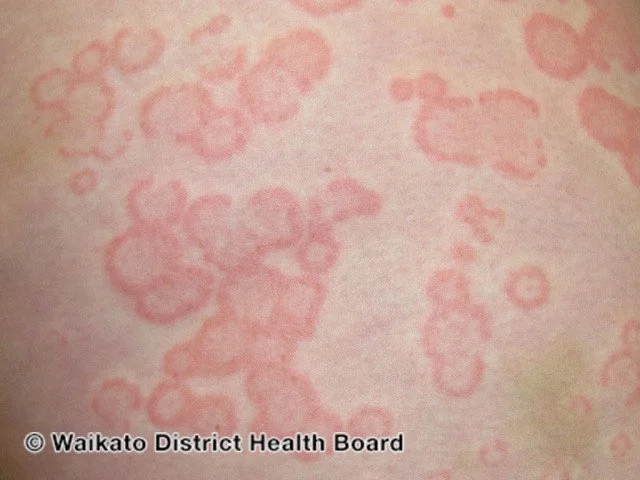
Hives will come and go with individual lesions not lasting longer than 24 hours.
Credit: DermNet NZ
Hives can affect any part of the body including the hands and feet.
Credit: DermNet NZ