Folliculitis
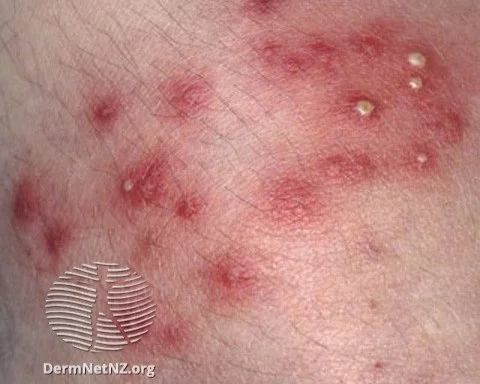
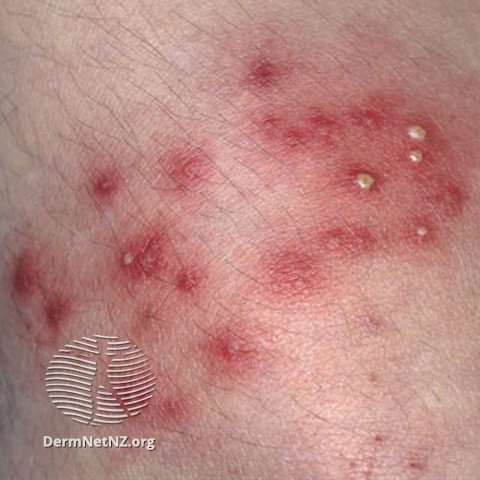
Folliculitis, which often looks like inflamed, pimple-like bumps on the body or scalp.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is folliculitis?
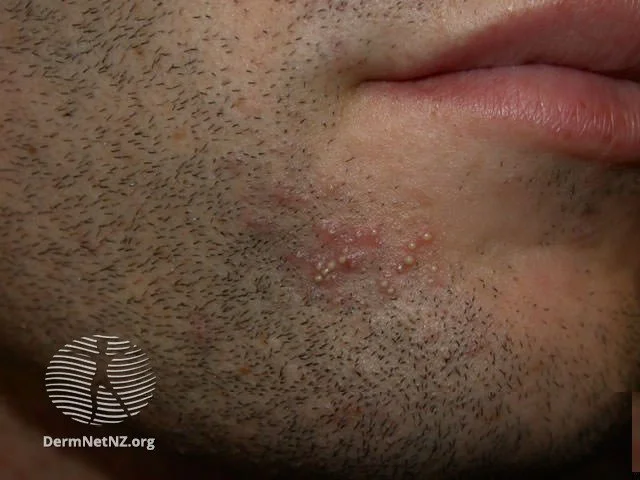
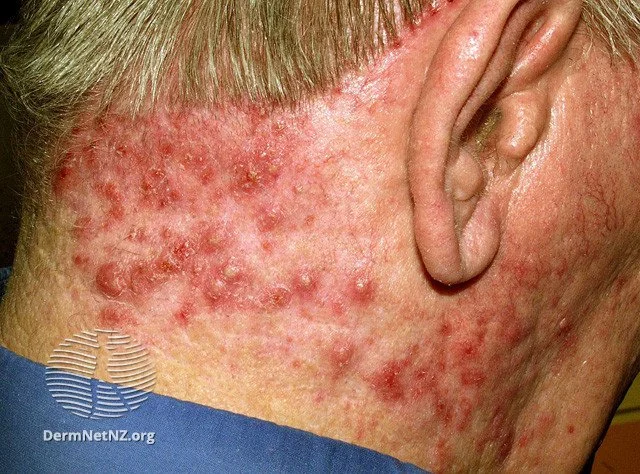
Folliculitis refers to the inflammation or infection of hair follicles, manifesting as small red or pus-filled bumps. Often tender to touch, these bumps can emerge on any hair-bearing region such as the face, chest, back, limbs, or scalp.
What causes folliculitis?
The onset of folliculitis can be linked to infections, skin irritations, blocked pores, certain dermatological conditions, or hair regrowth post shaving, waxing, or plucking. Potential causative agents encompass:
Bacteria: Notably Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Yeasts: Such as Malassezia or Candida albicans.
Fungus: Leading to conditions like tinea barbae.
Viruses: The Herpes simplex virus, for instance.
Parasites: Like Demodex mites.
Furthermore, certain ailments are associated with folliculitis:
Folliculitis decalvans
And others
What are the symptoms of folliculitis?
The hallmark of folliculitis is the presence of red or pus-filled bumps surrounding a hair follicle. Exclusively appearing on hair-bearing regions, the adjacent skin might display redness, itchiness, or sensitivity. While generally superficial, in rare cases, deeper skin abscesses may develop.
How do I treat folliculitis?
Addressing folliculitis necessitates understanding its root cause. After identifying the underlying issue, suitable treatments can comprise:
Oral antibiotic medications
Oral antifungal treatments
Isotretinoin, for certain forms of acne
How do I prevent folliculitis?
Though total prevention may be challenging, adopting the following strategies might mitigate the risk:
Avert prolonged skin occlusion
Pause hair removal in affected zones
Opt for non-comedogenic moisturizers
Consider laser hair removal as a long-term solution
Folliculitis can occur sometimes as a result of shaving.
Credit: DermNet NZ
Folliculitis is often bacterial in nature, but sometimes can be fungal or viral as well.
Credit: DermNet NZ