Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
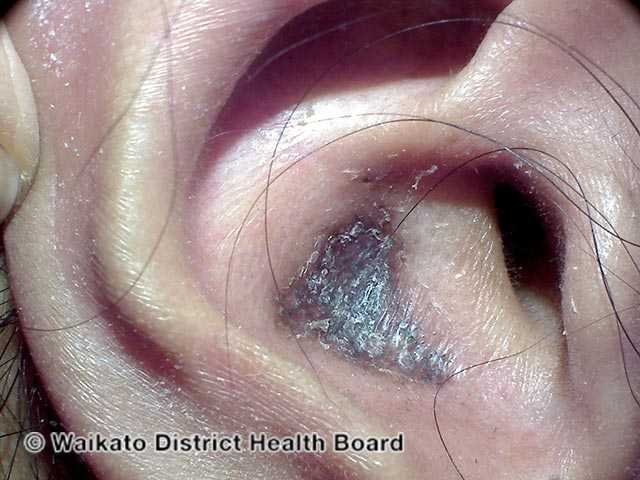
An example of conchal bowl involvement in discoid lupus, which shows up as violaceous plaques with scaling and dyspigmentation.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is discoid lupus?
Discoid lupus represents the most common form of chronic skin lupus. Most patients with discoid lupus only have lupus symptoms in their skin, but a minority (5%-25%) may develop systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Distinctively, discoid lupus manifests as enduring, reddish, scaly disc-shaped patches, predominantly on the scalp, face, and ears. These patches can lead to alterations in skin pigmentation, scarring, and alopecia.
What causes discoid lupus?
The etiology of discoid lupus remains ambiguous, yet several factors are speculated to contribute:
Genetic predispositions
Sun exposure, typically manifesting weeks post-exposure
Tobacco smoke
Hormonal influences
What are the symptoms of discoid lupus?
While discoid lupus primarily presents in the facial region (localized), it can also be widespread (generalized), spanning both above and below the neck. Commonly affected areas include the nose, cheeks, earlobes, and ear canals, with possible involvement of the lips, oral cavity, nose, and eyelids. The transition from discoid lupus to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is observed in 5%-25% of cases, often with milder symptoms compared to primary SLE cases. Typical manifestations include:
Initial presentation of dry, erythematous patches
Evolution into edematous, reddened, or hyperpigmented plaques with scaling
Hair follicles showcase white plugs upon scale removal
Advanced lesions resemble scars, often hyperpigmented, with a central hypopigmented region
Hair loss, either transient or permanent, is linked to scalp lesions
How do I treat discoid lupus?
Therapeutic strategies for discoid lupus often overlap with those for SLE. However, emphasis is laid on localized treatments in lieu of systemic interventions. Available treatments encompass:
High-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroid injections
Topical agents like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus
Retinoids, such as isotretinoin and acitretin
Oral corticosteroids like prednisone during acute exacerbations
Other immunomodulatory agents, including azathioprine, mycophenolate, and cyclophosphamide
Thalidomide
Pulsed Dye Laser therapy
How do I prevent discoid lupus?
Proactive measures to reduce discoid lupus flare-ups include:
Rigorous sun protection using appropriate attire, accessories, and broad-spectrum sunscreens with SPF 50+
Sun avoidance complemented by Vitamin D supplementation
Discontinuation of smoking
An example of hypopigmented areas due to inflammation in discoid lupus
Credit: DermNet NZ
Discoid Lupus can affect the scalp and cause scarring hair loss.
Credit: DermNet NZ


